Controlling JavaScript Malware Before it Runs
We've posted a number of stories lately about various exploit kits and the malware they post. What I'm seeing lately is a bit of an uptick in the use of Javascript by these exploit kits.
Why might this be, you ask? Isn't Javascript contained and hopefully secured within the browser sandbox? Aren't we protected by the combined security smarts of Microsoft, Mozilla and Google, right? We-e-e-e-l, the short answer is NO. If the Javascript arrives in an inbound email, and one of your windows based users clicks it, it doesn't execute in the browser, it executes inside of the windows shell (the same shell used by cscript.exe or wscript.exe)! So as Brad Duncan (another of the ISC Handlers) pointed out, this isn't really a Javascript *exploit*, it's Javascript as nature intended it to be (Brad knows way more about malware than I ever will).
We can see this in the registry at:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\FileExts\.js\OpenWithProgids
and you'll find "jsfile" as a key
computer\hkey_classes_root\.js = jsfile
computer\hkey_classes_root\jsfile = wshext.dll
Or, when you check the file extension in explorer, Shazam!, it's Windows Script Host!
Not only that, cscript.exe is meant as an admin tool, so all of the Javascript protections that we take for granted in our browser are ABSOLUTELY NOT in play. All kinds of new (or rather old) features that aren't allowed in the browser now work again. For instance, javascript executed in cscript can create a tcp client or a tcp server. Like perhaps to pull malware, maybe crypto-malware down, then install it. Or to create a basic tcp backdoor or a reverse-shell backdoor.
Worse yet, when you receive a JS file in an email, you'll see an icon that makes it look like it's a text or document file of some kind. On top of all of that, what we're seeing as a common SPAM practice that makes this more confusing for the folks reading their mail is a "double extension" approach - so these are arriving as "corporate layoffs.doc.js", "bonus Q2.xls.js" or "ups shipping notice.pdf.js" - when this shows up in your mail client, by default Windows (not so helpfully) won't display the "known file extension" of js, so your folks will see these as docs, excel sheets or pdf files.
.png)
So how can we as system administrators protect our users? Out of the gate we should strip out attachments of type .JS in emails at the SPAM gateway - there's no good reason to be emailing javascript files in and out of the organization (in almost all cases)
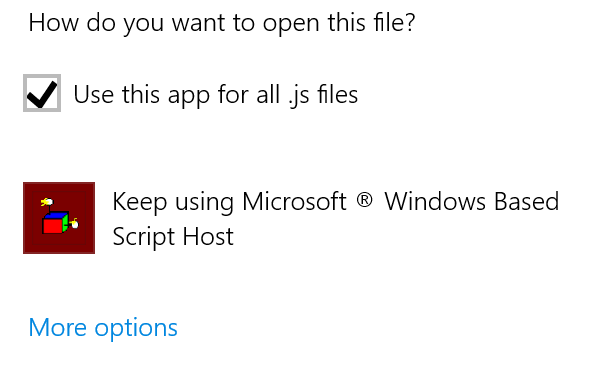
In the spirit of "defense in depth" though, let's assume that one of our trusted business partners (who might be whitelisted in the spam filter) or one of our internal users (internal mail doesn't typically go through the spam filter) is already compromised. How do we protect our users in those scenarios? Let's re-associated .JS file with something that won't actually execute the file - how about notepad?
To do this for a single workstation, right-click on a .js file, and open it with notepad, be sure to click the "always use the selected program to open this kind of file" radio box when you do that.
For an entire organization, you can force the file association in Group Policy, at Computer Configuration / Preferences / Control Panel Settings / Folder Options, then add "New" / File Type
You can see here that we can change how the file opens, and even change the icon that's being displayed.
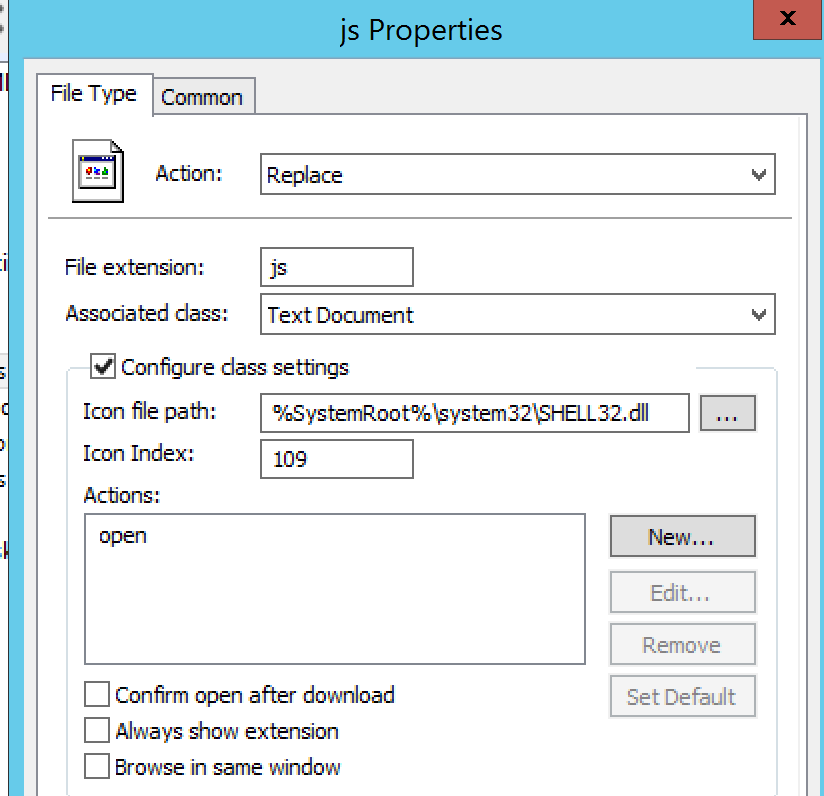
Now when we receive some malicious javascript in our inbox, it'll look very different. And when your folks click on the file, that advanced persistent malicious "hello.js" file below will display rather than execute.
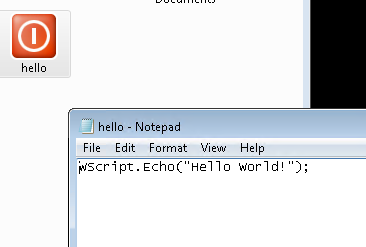
So if you're walking around the office, you can look for the screen that has 10 or 12 notepad files of code open, and feel good that there's one that didn't get infected! Or more likely (and sadly), check that machine to see how *else* they found to get infected :-)
===============
Rob VandenBrink
Compugen
.PNG)


Comments