Tool to Detect Active Phishing Attacks Using Unicode Look-Alike Domains
[This is a guest diary contributed by Remco Verhoef. If you would like to contribute a guest post, please let us know via our contact page]
Currently there is a campaign going on where phishing attacks will use domains that look exactly like safe domains by using Punycode domains. (https://www.wordfence.com/blog/2017/04/chrome-firefox-unicode-phishing/)
This is called a homograph attack. The Punycode domains will start with xn-- prefix and browsers will show the decoded Unicode domain name in the address bar where the Unicode characters (homographs) used appears like the original characters.
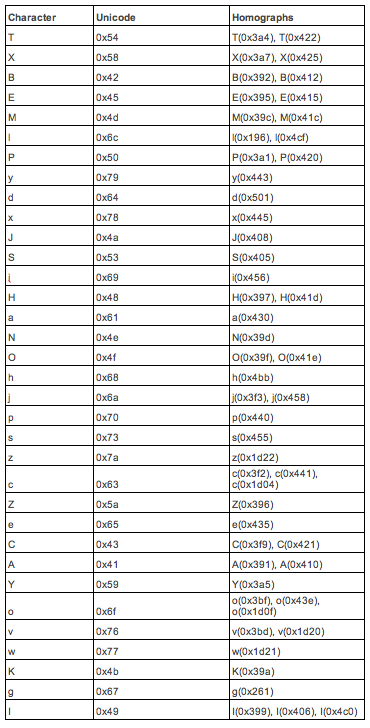
I wrote a program to look for similar characters within a font, comparing exact matches of glyphs. Outputting the table below. It shows the (ASCII) character with the homograph(s). Each font could have different homographs. For Phishing campaigns not only homograph domains could be used, but also the glyphs with small changes. Besides the program to built the table, I’ve created a program that will verify domains to see if they will have a (visually) exact match with a safe domain. Both programs are currently not open source, but will upon request.
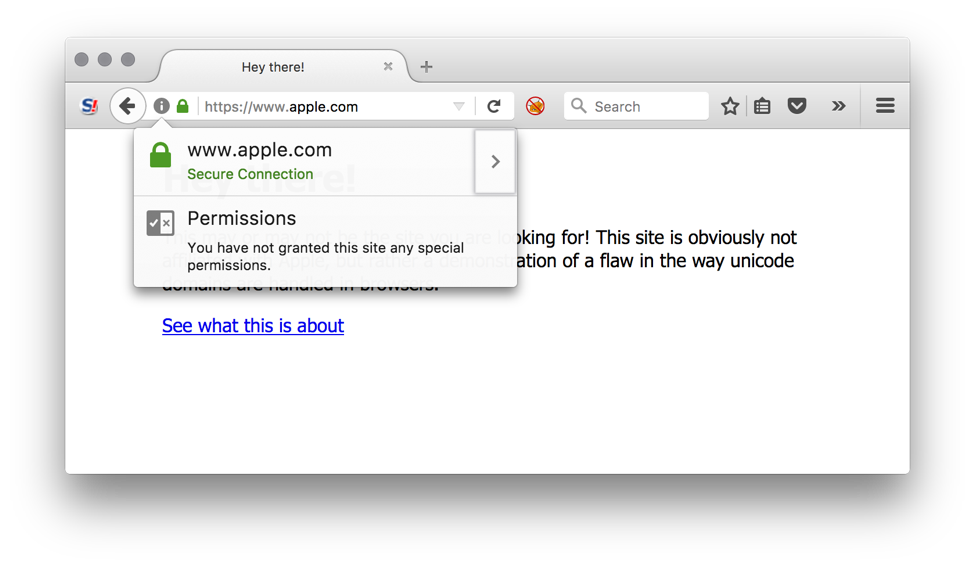
When using for example URL (courtesy of Xudong Zheng) https://www.xn--80ak6aa92e.com/, you’ll see (in Firefox and Chrome) in your address bar https://www.apple.com/.
It is possible to request SSL certificates (using e.g., Let’s Encrypt) with Punycode domain names, making this attack even more dangerous. The address bar will appear secure and contain the safe domain name. Impossible to recognize the difference.
We’ve found the following safe domain alternatives. These are probably tip of the iceberg. These domains are exact counterparts of the safe domains. Some companies register a lot of the homograph domains themselves. Google for example, but it seems they forgot a few.
|
Punycode domain |
Unicode domain |
Safe domain |
Registrar safe domain |
Registrar homograph domain |
|
CI Investments Inc. |
Privacy Protection |
|||
|
google.com |
|
Proxy Protection LLC |
||
|
googie.com |
|
WHOISGUARD PROTECTED |
||
|
instagram.com |
Instagram, LLC |
WHOISGUARD PROTECTED |
||
|
telegram.com |
Gatehouse Media, LLC |
Shield Digital Security Group |
||
|
whatsapp.com |
Whatsapp Inc. |
Rafael Fernández López (private) |
||
|
youtube.com |
MARKMONITOR INC. |
Anna Potepa (private) |
||
|
apple.com |
CSC CORPORATE DOMAINS, INC. |
Contact Privacy Inc. Customer 1241053230 |
||
|
ci.com |
CI Investments Inc. |
Privacy Protection |
Firefox, Chrome, and Opera browsers are vulnerable to the homograph attack, whereas the latest Chrome will contain a fix for this issue. Within Firefox the support for Punycode can be disabled by navigating to about:config and disabling “network.IDN_show_punycode”.
Resources:
https://www.wordfence.com/blog/2017/04/chrome-firefox-unicode-phishing/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IDN_homograph_attack
https://www.xudongz.com/blog/2017/idn-phishing/
https://isc.sans.edu/forums/diary/This+Article+is+Brought+to+You+By+the+Letter+12494/20319
Detecting SMB Covert Channel ("Double Pulsar")
With Friday's release of additional Shadowbroker tools, a lot of attention was spent on exploits with names like "Eternalblue", which exploited only recently patched vulnerabilities. Another item of interest however, is the command and control channel used to communicate with systems post exploitation.
One covert channel, "double pulsar", is designed to particular for systems that are vulnerable to Eternalblue. The covert channel uses SMB features that have so far been not used, in particular, the "Trans2" feature. Trans2 is short for "Transaction 2 Subcommand Extension", and its use can be seen as part of the exploit packet capture I posted in our earlier diary.
In packet 13 of the pcap, the system running the exploit sends a "trans2 SESSION_SETUP" request to the victim. This happens before the actual exploit is sent. The intent of this request is to check if the system is already compromised. Infected or not, the system will respond with a "Not Implemented" message. But as part of the message, a "Multiplex ID" is returned that is 65 (0x41) for normal systems and 81 (0x51) for infected systems. If a system is infected, then SMB can be used as a covert channel to exfiltrate data or launch remote commands.
Countercept released a python script that can be used to scan systems for the presence of this backdoor. See https://github.com/countercept/doublepulsar-detection-script .
---
Johannes B. Ullrich, Ph.D. , Dean of Research, SANS Technology Institute
STI|Twitter|


Comments