Increased Number of Configuration File Scans
Today, automation is a crucial point for many organizations. In cloud environments, in containers, many apps are deployed automatically, for example, to face a sudden peak of activity or to reduce costs. Automation means that everything must be pre-configured: specifications of the applications but also critical information to interact with the hosting platform (credentials, API keys, secret keys, …)
Such information is often stored in environment files. The best example is probably the “.env’ file used by Docker. Such files contain credentials in key-value format for services. They should be stored locally and not be uploaded to code repositories. The verb “should” is the problem. Many developers include .env files in online repositories and, when the application is deployed, they become publicly available!
Of course, bots are looking for such files. I detected a recent peak of activity in my logs:
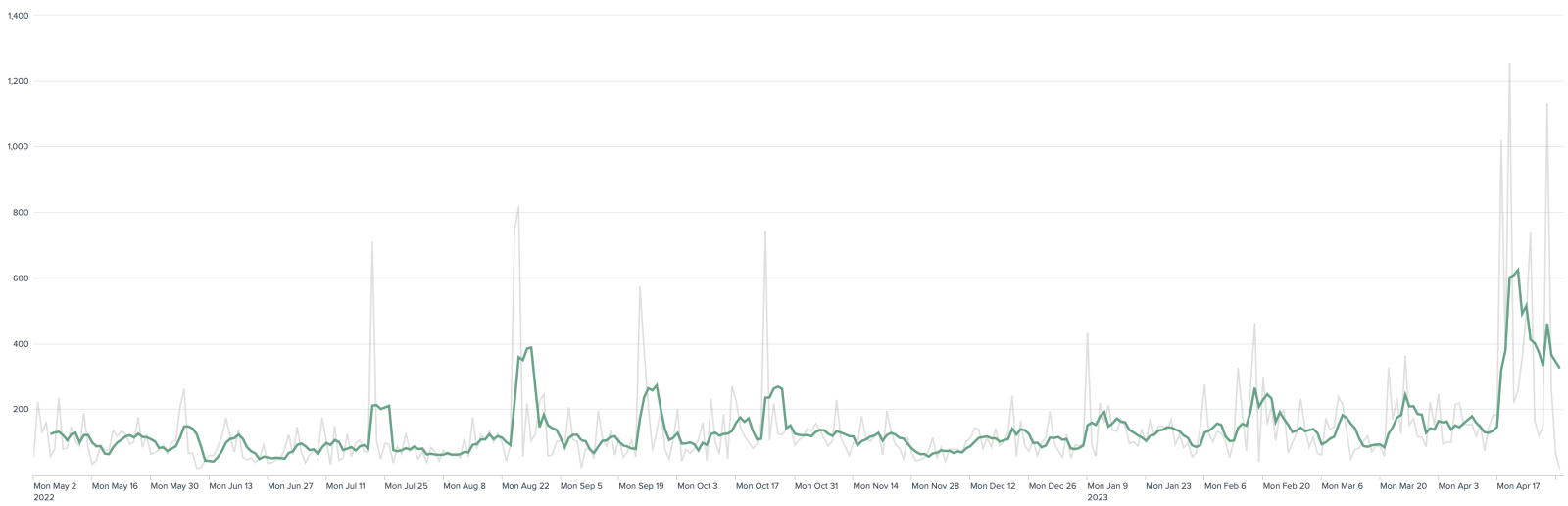
How to protect against this? First, education is key, and developers must be aware of the danger of publishing details about their environment in the wild. In parallel to awareness, access to dangerous files can be denied using simple rules, for example, with Apache:
<Files ~ "\.(env|json|config.js|md|gitignore|gitattributes|lock)$">
Order allow,deny
Deny from all
</Files>
Which .env files are searched by bots? Here are the top 10 URIs from my logs:
| /.env | 22004 |
| /laravel/.env | 2371 |
| /web/.env | 1610 |
| /demo/.env | 1532 |
| /admin/.env | 998 |
| /app/.env | 989 |
| /api/.env | 826 |
| /core/.env | 808 |
| /backend/.env | 665 |
| /public/.env | 495 |
Xavier Mertens (@xme)
Xameco
Senior ISC Handler - Freelance Cyber Security Consultant
PGP Key
| Reverse-Engineering Malware: Advanced Code Analysis | Online | Greenwich Mean Time | Oct 27th - Oct 31st 2025 |


Comments